Lesson Plan
Luscious Leaves
Grade Level
Purpose
Students examine the functions of plant leaves and identify leaves as edible parts of some plants. Grades 3-5
Estimated Time
Materials Needed
- Leaf Tasting Investigation Worksheets for each student
- Handwashing area
- Butcher paper or chalkboard
- Five edible leaf samples: lettuce, kale, spinach, parsley, Swiss chard; for each group.
- Leaf Tasting Investigation activity sheet
Vocabulary
diet: the kinds of food that a person, animal or community habitually eats
farmer: person who owns or manages a farm, cultivates land or crops, or raises animals
photosynthesis: the process by which plants convert carbon dioxide, water, and light energy into sugars and oxygen in order to store energy; the opposite of cell respiration
Did You Know?
- Kale is considered to be closer to wild cabbage than most domesticated forms of vegetables.
- Kale is an excellent source of vitamin K, which controls inflammation in the body.
- Although paler in color than other leafy greens, cabbage is a great source of cancer-fighting compounds and vitamin C.
- Iceberg lettuce is mostly water, but it is the most popular leafy green in the United States. American eat about 17 pounds of it every year.
Background Agricultural Connections
This lesson is part of a series called, Edible Plant Parts. These lessons allow students and teachers to examine the six basic plant parts—roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds—in a unique way. Through hands-on activities, students will learn about the different plant parts, as well as how to include fruits and vegetables into their daily meals as part of a healthy diet. Students will also learn about agriculture and the people who produce our food. The remaining lessons can be found at the following links:
 Why People Need Plants
Why People Need Plants- Dig 'Em Up
- Snappy Stems
- Luscious Leaves
- Fabulous Flowers
- Freshest Fruits
- Supreme Seeds
- Edible Plant Game
- Eat 'Em Up
The main function of a plant’s leaves is to gather energy from the sun to carry out photosynthesis and make food for the plant. During
photosynthesis, leaves use light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugar.
Many leaves of plants are edible and are grown for food. Edible leaves include cabbage, lettuce, grape leaves, parsley, spinach, mustard greens, and Swiss chard. These foods a healthy addition to our diet. We are fortunate to have many different varieties of edible leaves grown by farmers in the United States. As a result, we have many healthy options when shopping for produce in our supermarkets or farmers markets.
Make sure students understand that not all leaves are edible and that they should never eat anything they are unsure of unless it is approved by a responsible adult.
Engage
- Draw a basic diagram of your body. Circle the areas or draw arrows to identify parts of your body which benefit from the nutrients in leafy green vegetables and list the benefit (e.g., vitamin A assists with good vision).
- Describe why it is important to eat fresh vegetables (like leafy, green vegetables) rather than just taking a vitamin or only eating fortified foods.
Explore and Explain
Activity 1:
- Discuss the functions of plant leaves with your class. Possible topics include making food for the plant, decomposing and adding nutrients to the soil, and providing habitats for animals. After you talk about the functions of leaves, ask your students if they can think of any edible leaves that people like to eat. Make a list on the board. Explain that leafy greens are part of a healthy diet. Students ages 4-8 need 1 ½ cups of vegetables per day and students ages 9-13 need 2 to 2 ½ cups of vegetables per day. Two cups of raw leafy greens is considered one cup from the vegetable group.
- Tell your students that today they are going to investigate five different types of edible leaves, by tasting, smelling, measuring, and observing. They will also compare their nutritional value by looking at their levels of vitamin A per serving.
- Tell students that vitamin A is important for maintaining good vision, fighting infection, supporting cell growth, and keeping skin healthy. Research has shown that consuming foods rich in vitamin A may even prevent some kinds of cancer.
- Organize students into groups of three or four and have them wash their hands before sitting in their seats. Distribute worksheets to each student and tell them that they will be using the Leaf Tasting Investigation Chart for the next part of the lesson.
- Show your class one edible leaf and show them where it is listed on the chart. Demonstrate how you would like each group to record the color, texture, smell, taste, and length of each leaf in the chart. Use a ruler to measure the length of each leaf. Examples of texture could include smooth, fuzzy, bumpy, sandpapery, slippery, etc. Be sure to discuss possible vocabulary with your students before they begin describing leaf texture, smell, and taste. Distribute a washed sample of the leaf to each group and guide them through the data collection. When students have recorded data in their charts, instruct them to tear off a small piece of the leaf to taste.
- Repeat this procedure with the remaining four leaves and have students fill out the questions on the chart.
Activity 2:
- Have students fill in their chart to compare the vitamin A levels of the five leaves they tasted in part one. Students should use the chart template on the back page of their tasting chart.

- Write these vitamin A % values on the board for all students to see (see table above).
- Go through one example with the class and then have them work in their groups to fill in the bar graphs for the remaining leaves. Discuss which edible leaves are the best source of vitamin A and why this is an important nutrient.
ELL Adaptations:
- Model the Think, Pair, Share method: Have students turn to a partner and say, "What kind of leaves do we eat?" Explain that their partner should then respond, "We eat lettuce, spinach, and other examples."
- When introducing new vocabulary words, show students an example of the object.
- Make a "word wall" of new vocabulary and have students cut out pictures from magazines to match the vocabulary words.
Elaborate
-
Give each student a leaf and a crayon. Instruct students to remove the paper wrapping from the crayon. Have each student make a leaf rubbing by placing the leaf under a piece of paper and then rubbing the side of their crayon over the top of the paper. The image of the leaf will be visible. Mount the rubbings on colorful paper.
-
Have students plant a lettuce or kale seed in a plastic cup. After the seedlings sprout, students can take them home to trasplant and share healthy, leafy greens with their families.
-
Bring in fresh and dried herbs. Discuss how they look and taste.
-
Make an edible leaf salad that the whole class can enjoy at the end of the lesson. For homework, have students track how many servings of leafy greens their family eats in a week.
-
Discuss the following chart with the class and research why these nutrients are important in a healthy diet.
There are many nutritional benefits of eating fresh, green, leafy produce!
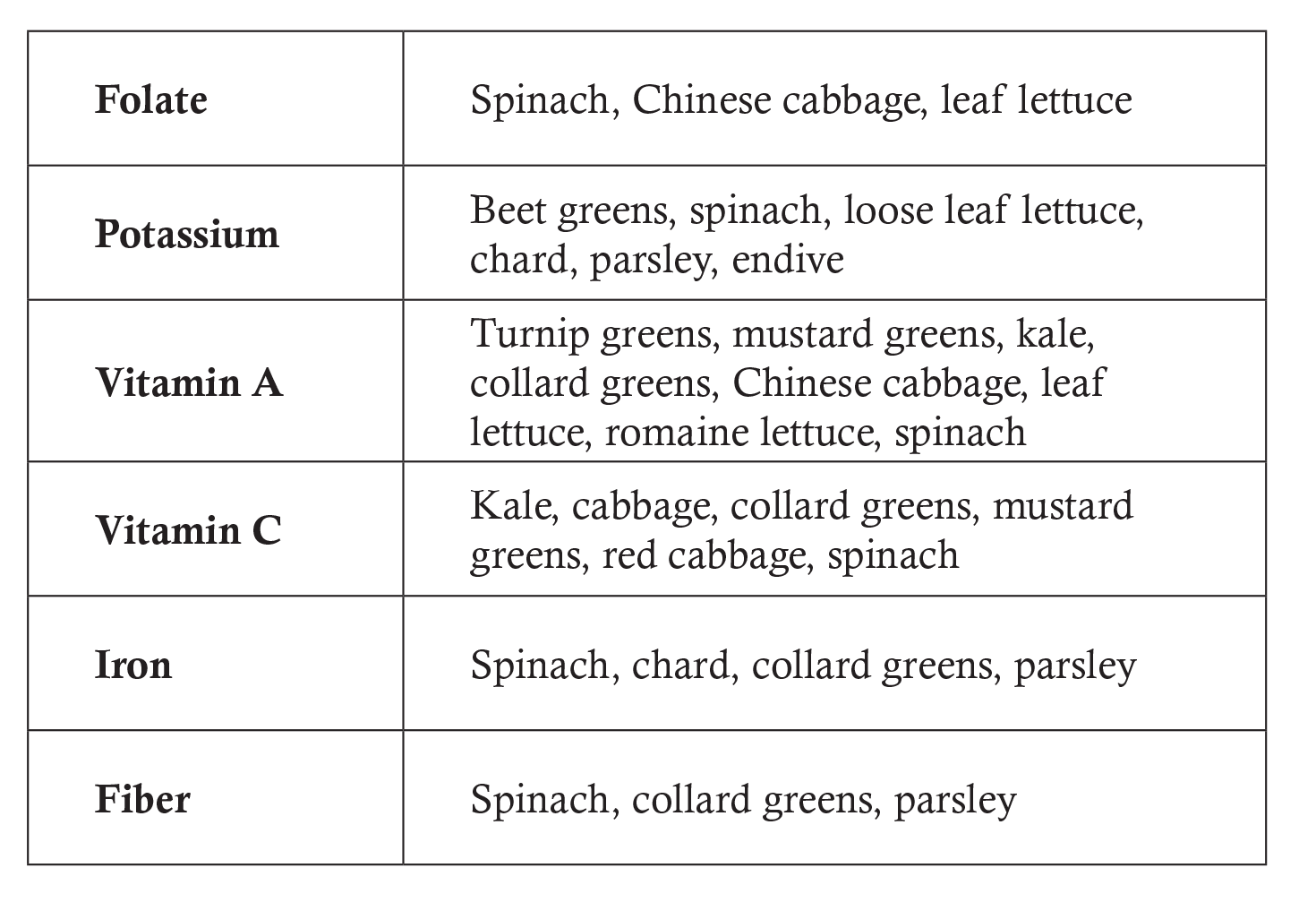
Evaluate
After conducting this activity, review and summarize the following key concepts:
- Farmers grow some plants for their edible leaves.
- Many edible leaves are a delicious source of vitamin A, and many other nutrients that are important in a healthy diet.
Acknowledgements
This lesson update was funded by a grant from the Network for a Healthy California.
Executive Director: Judy Culbertson
Illustrator: Erik Davison
Layout & Design: Nina Danner
Copy Editor: Leah Rosasco
Recommended Companion Resources
- A Weed Is a Flower: The Life of George Washington Carver
- Edible Plant Game
- Farming in a Glove
- Growing Microgreens
- How Things Grow
- Nutrition Ag Mag
- Plants Feed Me
- The Magic School Bus Gets Planted: A Book About Photosynthesis
- The Real Reason Leaves Change Color in the Fall
- Timelapse: Photosynthesis Seen from Space
- Tops & Bottoms
- Up, Down, and Around
- What Do Plants Need to Grow?
Author
Organization
| We welcome your feedback! If you have a question about this lesson or would like to report a broken link, please send us an email. If you have used this lesson and are willing to share your experience, we will provide you with a coupon code for 10% off your next purchase at AgClassroomStore. |